Latest Cassini findings confirm: Saturnian system is young!
An upper limit of 100 million years is far shorter than previously thought, and collapses the secular timeline for the entire solar system.

A ‘hundred million years’ sounds like a long time, but for secular materialists, it’s not. As an upper limit, it’s a catastrophe for their ideology. Unless they can believe that a young Saturn, complete with rings and 62 moons, formed separately within a pre-existing old solar system (which they would never accept), such a ‘young’ age takes down the whole edifice of planetary evolution, and with it, chemical and Darwinian evolution on planet Earth.
Recent scientific papers confirm that Saturn’s rings and its moons Titan and Enceladus cannot be older than 100 million years, and could be as young as 10 million years (that is, in their secular estimation; they could be a lot younger).
To show why this upper limit is so devastating to their old-age worldview, in some of my talks, I ask a volunteer to help me stretch out a 14-metre (45-foot) rope across the stage. It represents 4.5 billion years, i.e. the evolutionary/naturalistic age of the Solar System. I ask them how much of the rope represents 100 million years. The surprising answer is: 30 cm (one foot)! And 10 million is 1⁄10 of that, just 30 mm (1.2 in). One million years is such a tiny sliver, it almost disappears from view. Then I ask them, “If the rings were only around for 1⁄45 the time represented by this rope, what was going on for the other ⁴⁴⁄45? Did those 4.4 billion years even exist?”
Saturn is not the only planet that looks vastly younger than old-agers expect. Age problems could be multiplied for all of the other planets, especially our own planet Earth and its moon.1 Indications of old age are the exception, not the rule. But since Saturn was my specialty when working at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and has the most recent news, let’s take a closer look at the Saturn system and what scientists have found.
Remember, 100 million years is our friend, because it’s an upper limit, meaning the objects cannot be older than that—but can be younger. We don’t have to agree with the date, but such a ‘young’ date demolishes solar system evolution.
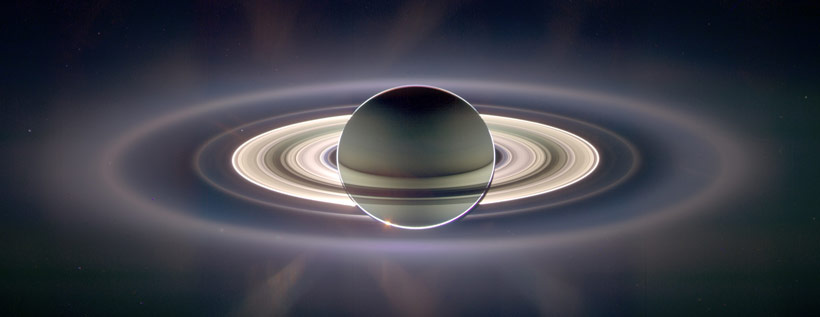
Rings
In June 2019, Science magazine published some of the most recent findings from the Cassini mission, which ended 15 September 2017. The rings have ‘youth’ written all over them. In a Perspective article about “The origin of Saturn’s rings and moons”, Shigeru Ida from Tokyo University summarized conclusions about the rings, using the word young five times.2 “[T]o be consistent with the observed clean rings, the rings must be as young as 10 to 100 million years,” he said, echoing the opinion of 13 Cassini scientists in another paper:3 “The low value of the ring mass suggests a scenario where the present rings of Saturn are young, probably just 10 million to 100 million years old, to be consistent with their pristine icy composition.” Lead author Luciano Iess told the BBC News this is like “yesterday” compared to the (supposed) age of Saturn.4 A third paper by 25 leading ring experts agrees: “Together, these results show that Saturn’s rings are substantially younger than the planet itself and constrain models of their origin.”5
What can scientists do to maintain their belief that Saturn is billions of years old? They either have to make the initial rings much more massive than earlier thought, or propose an almost miraculous event that formed the rings relatively recently. Both proposals require unreasonable faith.
The first is contradicted by the ‘clean’ appearance of the rings, which are 95% pure water ice. With all the dust and debris in space, if they had been around for billions of years, they should be much ‘dirtier’.
The second makes the rings an extremely lucky event (in long-age terms) that happens to coincide with the sliver of cosmic time in which there are humans who can see them from Earth. To materialists, who deny human exceptionalism, this kind of coincidence is philosophically distasteful, but what else can they say?
“Models for a young ring system invoke the chance capture and tidal disruption of a comet or an icy outer Solar System body, suggesting that catastrophic events continued to occur in the Solar System long after its formation 4.6 billion years ago,” the 25 experts say. Shigeru Ida, however, worries about “the low probability of an encounter with a Kuiper Belt object less than 2 billion years ago,” which would be “very rare” so late after the formation of the solar system. The secularists are stuck with believing in improbable, almost miraculous luck. Instead, Scripture tells us of an intelligent Creator who had both the necessary and sufficient power to create beauty and diversity in His universe.
Titan
Saturn’s large, smog-shrouded moon Titan, has long been a problem for old-agers. In the 1990s, they had predicted a global ocean of ethane on the surface. Instead, some lakes were found at the poles, but the equatorial regions were girded with ‘sand dunes’. The ‘sand’ in these dunes is made of ice crystals coated with complex organic molecules, like acetylene.
Scientists publishing in Science Advances were able to recreate growth of “benzene, naphthalene, and phenanthrene—prospective building blocks of the organic dune material” by simulating exposure of acetylene ices to cosmic rays. The process was so efficient, they were able to get these materials to form in the lab over time periods extrapolated to Titan conditions from 10.4 to 104 years. “Therefore, this study reveals that even over a relatively short time scale of about 104 years, PAHs [polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons] as complex as phenanthrene can be synthesized on Titan’s surface”, they say.6 This production by cosmic rays would augment atmospheric production, not requiring billions of years for the dunes to form. Incidentally, no solution has been found for the missing ethane lakes, which remains a serious falsification of old-age predictions.
Enceladus
The moon Enceladus, about 1⁄7 the diameter of our own moon, stole the show at the Saturn mission, captivating scientists and public alike with its south-pole geysers. Could this tiny moon really have been spewing ice at supersonic speeds for billions of years? The output is so voluminous, it contributes ions to Saturn’s magnetosphere, and has a significant effect on the planet’s magnetic field. It also creates the broad E-ring around Saturn from the leftover particles that don’t land back on the moon itself.
Now, Cassini radar data has shown that Enceladus is spray-painting the other moons! The words ‘young’ or ‘youth’ appear 10 times in an open-access paper about this in Geophysical Research Letters.7 Based on the depth of ices found on Mimas, Tethys, Dione and Rhea, these scientists estimate the ices accumulated in less than 200 million years. But even that relatively young (for solar system evolution theories) result may be too long; if Enceladus is also spewing ice directly at these bodies, this “suggests that current models underestimate the rate of deposition of particles from the E-ring at the surface of Enceladus’s neighbors.” Consequently, the radar albedo measurements indicate that these “middle-sized satellites of Saturn are younger than previously thought.”
These are not the only indications of youth at Saturn, but together, they undermine the billions of years needed by secular scientists for their evolution narratives. Titan, Enceladus, and Saturn’s rings stand as silent witnesses against the evolutionary timeline. While Cassini data cannot directly corroborate the 6,000-year creation age deducible from the Bible, they seriously undermine secular creation myths (see 2 Corinthians 10:5), closing off options for unbelief. And if the leading argument for doubting the Bible (i.e., evolution over billions of years) is out of time, honest seekers can start confidently at Genesis 1 and proceed to the Cross and Resurrection of Christ, and find eternal life.
References and notes
- Batten, D., 101 evidences for a young age of the earth and the universe; creation.com/age, 18 Sep 2019. Return to text.
- Ida, S., The Origin of Saturn’s Rings and Moons, Science 364(6445), pp. 1028–1030, 14 Jun 2019. Return to text.
- Iess, L. et al., Measurement and implications of Saturn’s gravity field and ring mass, Science 364(6445):eaat2965, 14 Jun 2019. Return to text.
- Amos, J., Saturn’s spectacular rings are ‘very young’; bbc.com, 17 Jan 2019. Return to text.
- Tiscareno, M. et al., Close-range remote sensing of Saturn’s rings during Cassini’s ring-grazing orbits and Grand Finale, Science 364(6445):eaau1017, 14 Jun 2019. Return to text.
- Abplanalp, M. et al., Low-temperature synthesis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Titan’s surface ices and on airless bodies, Science Advances 5(10):eaaw5841, 16 Oct 2019. Return to text.
- Le Gall, A., West, R., and Bonnefoy, L., Dust and snow cover on Saturn’s icy moons, Geophysical Research Letters 23 Oct 2019. Return to text.







Readers’ comments
Comments are automatically closed 14 days after publication.