The singularity—a ‘Dark’ beginning
Did the universe form spontaneously from nothing?
“The universe burst into something from absolutely nothing––zero, nada. And as it got bigger, it became filled with even more stuff that came from absolutely nowhere. How is that possible? Ask Alan Guth. His theory of inflation helps explain everything.”—front cover of the April 2002 issue of Discover magazine.
“Spontaneous creation of the universe from nothing”1 is the title of a 2014 paper authored by He, Gao and Cai, published in the American Physical Society journal Physical Review D, one of America’s most prestigious journals dealing with physical theory. It purports to outline a so-called mathematical proof that the universe did indeed burst into something from nothing.
There is also a website extolling the wonders of this discovery in an item titled, ‘A Mathematical Proof That The Universe Could Have Formed Spontaneously From Nothing’ with the subtitle, ‘Cosmologists assume that natural quantum fluctuations allowed the Big Bang to happen spontaneously. Now they have a mathematical proof.’2
That website lists the evidence in support of the big bang cosmogony:
- the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation often claimed as an ‘echo of the big bang’ or ‘fossil radiation’ from that explosion;3
- the expansion of the cosmos or space itself, which, when imagined by extrapolating it backwards, suggests its origin in a big bang, i.e. a dimensionless point or a singularity;4 and
- the abundances of the primordial elements, such as hydrogen, helium-4, helium-3, deuterium and a few others, can all be calculated using the theory.5
Evolutionary cosmology is very much like evolutionary biology which tries to establish the origin of all living things over the past 3.8 billion years by an appeal to circumstantial evidence. The strongest parallel I see here is the fossils in the sedimentary layers that are supposed to represent millions to billions of years of history, yielding a sequence of organisms that allegedly evolved one from another over time.
This ‘fossil radiation’ (the CMB) is meant to be the leftover radiation from the big bang fireball, called the ‘last scattering surface’, after which light was freed from being trapped in the hot plasma, and travelled unimpeded throughout the universe. The expansion of space and the elemental abundances are more such circumstantial evidence. Though the CMB radiation was a prediction of George Gamow in 1948 (at 5 K later revised to 50 K) in support of the big bang, the elemental abundances could hardly be claimed as one. This is because the hydrogen/helium ratio for the universe had already been measured and was well known before Gamow’s students Alpher and Herman calculated what they should be, using a knowledge of declassified nuclear parameters after the close of World War II. This has been more correctly called a post-diction.
But there remains a truly huge puzzle. If there ever were a big bang, what caused it to bang? What started it off in the first place? For many years, cosmologists have believed that the universe just formed spontaneously, that the big bang was the result of some quantum fluctuations in which the universe just popped into existence from nothing. And I mean nothing; no space, no time, no energy, nothing.
The authors write in their article (bold emphases added):
“…we present such a proof based on the analytic solutions of the Wheeler-DeWitt equation…once a small true vacuum bubble is created by quantum fluctuations of the metastable false vacuum, it can expand exponentially no matter whether the bubble is closed, flat or open.”6
The proof they offer is a mathematical one. It is not the type of proof you might be expecting where a physical theory has been tested by development of a hypothesis which then is tested by an experiment through predictions the model makes. Not at all. In this case it relies totally on the unproven assumption that the mathematical model used somehow describes the universe an extremely short while after the big bang expansion was supposed to have begun. It also relies on the assumption that the real universe can be described by the mathematics and physical laws they assume in a putative past epoch where it is impossible to test anything.
The new approach extends the work of John Wheeler and Bryce DeWitt who developed a mathematical formalism, combining general relativity and quantum mechanics, in an effort to develop a quantum gravity theory for the early universe. This resulted in the famous Wheeler-DeWitt equation (WDWE),

Here the parameter a is the scale factor for the universe in a minisuperspace model; k is the spatial curvature, chosen as 1, 0, or-1 for positive (closed and finite), flat (Euclidean and infinite) or negative (open and infinite) bubbles respectively; and ψ is the wave function for the bubble universe. There is an infinite number of potential solutions, and additional information is needed to solve it for a particular system.
This model assumes the total energy content of the universe is zero, i.e. sum up all the matter and all forms of energy in the universe and the total will be zero. So it has been famously said that the big bang is the ‘ultimate free lunch’.
Paul Davies wrote:
“So science has done away with the need for a button-pushing creator who lives for eternity before making a Universe at a certain moment in time.”7
This new paper carries on the work of people like Hartle and Hawking8 who in 1983 mathematically showed that it is possible for time to be bounded in the past without there being a specific first moment. This comes from Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. It indicates that there is a sort of fuzziness to the beginning of time and space. In this way time takes on an imaginary quality and becomes a spatial coordinate. And they claim that the universe had many possible histories and we sample some of them, but none is unique.
What He et al. have done is mathematically show that once a small true vacuum bubble is created, it has a chance to expand exponentially, creating the observed universe. Note the use of the word ‘chance’. So you must understand they are talking about an ensemble of probable universes that might result from their model. Quantum theory deals only with probabilities of realising a possible outcome and in this sense the probability of a universe like ours might be very small indeed.
The obvious fact that this is mathematics and not testable on the real universe—the problem of cosmic variance—is not dealt with. That is the problem of the need to take an ensemble of real universes and see what the likely outcome of many possible creation episodes might be.
This new claim of spontaneous creation from nothing described by the WDWE is only valid for a > 0. The fact that the scale factor is positive and non-zero means this approach is only valid in a metastable quantum vacuum, i.e. such a vacuum must already exist. And this formulation presupposes the existence of the laws of physics, which are used in the derivation of the equation in the first instance.
So, as elegant as it might seem, the He et al. approach has not done away with a first cause. It has only assumed, quite explicitly actually, a certain form of the Hamiltonian for a bubble universe,
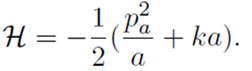
A Hamiltonian is the operator that corresponds to the total (kinetic and potential) energy in the system. In their universe the Hamiltonian is assumed to equal zero, i.e. that there is no energy there in the beginning, nothing! Their approach makes the presumption to use the current laws of physics. Also the analysis only applies in an ‘existing’ state as the scale factor is assumed to be time dependent and always non-zero.
The appeal to existing physics does not end there. To get an understanding of how the bubble universe explodes into the real universe a guidance relation is added. This comes from Bohmian quantum theory, by analogy with nonrelativistic particle physics and quantum field theory in flat space-time, where quantum trajectories are obtained. This ultimately tells you how the quantum potential changes as the bubble exponentially expands.
But for a universe like ours to come into existence by itself, without a Creator, it must create its own laws of physics as well as generate space and time and matter and energy from nothing, not from a pre-existing quantum vacuum, metastable or not. Even with their approach, the appearance of a universe would still require a pre-existing, intelligent agency/power.
No doubt their solution to this is to say that an infinite number of universes could probabilistically be created from the vacuum and it is only in this one that these laws of physics apply, etc. But that does not solve it because then you could not claim that all the laws used to explain this universe also explain the others of the multiverse coming into existence. How could you justify using our laws of physics to describe another universe where you have no knowledge of its physics? And you could not use our current laws to generate all those other universes which have different laws. It is sort of a Malmquist bias9 in choice of physics.
For others the solution to the problem of the first cause for this universe is:10
… that the universe is a three-dimensional “membrane” floating through a four-dimensional “bulk universe”.
They invoke higher dimensions and String theory to explain how their universe began and why it is. This is an appeal to new physics way beyond what we know now and can even hope to test experimentally, because it involves many more dimensions and takes place in some hypothetical past epoch and space.
This approach has been proposed with M theory, a form of String theory in as many as 11 dimensions (or even 28 in one form). Famously Leonard Susskind labelled the “M” in M theory as meaning ‘monstrous’. M Theory and its cousin, String theory, are not physics but mathematics, which lack any predictive power in the real world and hence are untestable. This seems to me to be a grab for a solution, to find an uncaused cause, because the big bang (with its unbiblical sequence of events) needs a first cause.
For the last 40 years String theory has gone on without a single experimental test or astronomical observation to verify any prediction. I once asked Prof. James Gates (Toll Professor of Physics and Director of the Center for String and Particle Theory at the University of Maryland) what he would say if no verifiable test of String theory were ever achieved. He answered that he would have just wasted the past 40 years of his life.
So, what caused the universe to explode? Alan Guth says:11
“In spite of the fact that we call it the big bang theory, ah, it really says absolutely nothing about the big bang. Ah, it doesn’t tell us what banged, why it banged, what caused it to bang. Ah, it doesn’t even describe—it doesn’t really allow us to predict what the conditions are immediately after this big bang.”
Paul Davies adds (bold emphases added):12
“Yet the laws [of physics] that permit a Universe to create itself are even more impressive than a cosmic magician. If there is a meaning or purpose beneath physical existence, then it is to those laws rather than to the big bang that we should direct our attention.”
‘Worship the creation’ is what comes across; the new religion of the scientific elite.
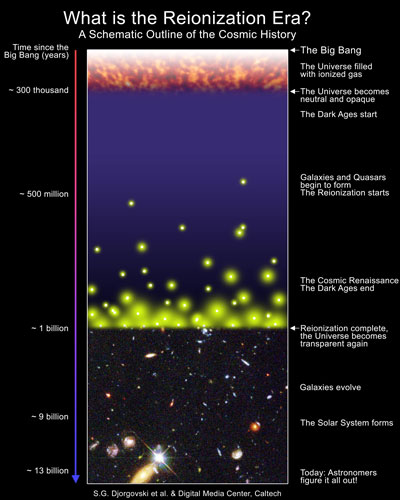
Some professing Christians have unwisely said this big bang creator must have been God, the biblical Creator. He started it off. Many such ideas have Him as a very impotent god, who had nothing much to do after that. It seems they are proposing Him as some sort of ‘god of the gaps.’ Modern big bang theory is an attempt to describe the universe without the Creator. It has no God. Therefore the universe supposedly begins in not only physical darkness (the Dark Ages occurring before the Reionization Era where galaxies were created, with the aid of dark matter, see Figure 1) but also spiritual darkness without any Creator.
Don’t be taken in by the technical bluff and bluster of the big bang proponents. It is not science in the usual repeatable laboratory experimental sense and it is very weak as one can never be certain one’s model actually describes reality. This is story-telling at its best. Figure 1 illustrates the story that is told, but all of it after the universe has begun. How did it begin?
The big God theory, from Genesis chapter 1 in the Bible, describes the origin of the universe as the work of the Creator (see Psalm 19:1), who has a great interest in His Creation. He divided the light from the darkness, which has both physical and spiritual meaning. The darkness later in the Creation symbolized those wicked angels and humans who rebelled against His wise counsel. The Creator is a God whom we can know personally. He is the great I AM, who was always there, the uncreated First Cause, and we can trust what He says, because He never lies (Numbers 23:19, Titus 1:2). He says He created the universe, in a particular historical sequence that differs from big bang philosophy. And there is nothing in the observations of the cosmos which is inconsistent with that account. I believe Him because He does not lie.
References and notes
- D. He, D. Gao, and Q-yu Cai, Spontaneous creation of the universe from nothing, Physical Review D, 89, 083510 (2014); arxiv.org/pdf/1404.1207v1.pdf. Return to text.
- See medium.com/the-physics-arxiv-blog/ed7ed0f304a3. Return to text.
- The expansion is not considered amongst cosmologists to be an explosion; more on that is planned in a later article. The CMB radiation is claimed as a prediction of the big bang model, though it is now acknowledged that McKellar measured it in 1941 before Gamow made his prediction (at a temperature of 5 K) in 1948 and before Penzias and Wilson discovered it again in 1964/1965 (at 3 K). Robert Dicke, P. J. E. Peebles, P. G. Roll, and D. T. Wilkinson interpret this radiation as a signature of the big bang. In 1952 Gamow predicted a temperature of 50 K (See A. McKellar, J. Kan-Mitchell, P.S. Conti, (1941). “Molecular Lines from the Lowest States of Diatomic Molecules Composed of Atoms Probably Present in Interstellar Space”, Publication of the Dominion Astrophysical Observatory (Victoria, BC) 7(6): 251–272. Gamow, G. (2004) [1961], The Creation of the Universe, Courier Dover Publications, New York, p. 40, 1961, 2004. Return to text.
- A later article is planned to deal with the issue of the expansion of space. Return to text.
- This is often claimed as a prediction of the big bang nucleosynthesis theory. Return to text.
- Ref. 1. Return to text.
- Davies, P., Is the Universe a free lunch?, 3 March 1996; independent.co.uk. Return to text.
- <http://web.uvic.ca/%7ejtwong/Hartle-Hawking.htm>The Hartle and Hawking No-Boundary Proposal, web.uvic.ca. Return to text.
- Malmquist bias is an effect in observational astronomy which leads to the preferential detection of intrinsically bright objects. The parallel is that if humans are able to describe the laws in another universe they are naturally biased to use our current laws to describe them. But if there is no God and those universes were randomly created with arbitrary laws why would our laws work in any sort of a description? The theorist has no choice and can only see those universes through our current laws of physics. Return to text.
- Has the Big Bang theory been busted?, 18 September 2013, news.com.au. Return to text.
- Alan Guth, Victor F. Weisskopf Professor of Physics at MIT, “Before, Meanwhile and After the BIG BANG—(M-Theory)”, youtube.com/watch?v=HOkAagw6iug, 11 September 2007. Return to text.
- Ref. 7. Return to text.






Readers’ comments
Comments are automatically closed 14 days after publication.